| TARGET | |
|---|---|
| SYNONYMS |
C-X-C Motif Chemokine 6;Chemokine Alpha 3;CKA-3;Granulocyte Chemotactic Protein 2;GCP-2;Small-Inducible Cytokine B6;CXCL6;GCP2;SCYB6 |
| DESCRIPTION |
Recombinant Human C-X-C Motif Chemokine 6 is produced by our Mammalian expression system and the target gene encoding Gly38-Asn114 is expressed with a 6His tag at the C-terminus. |
| DELIVERY |
In Stock |
| UNIPROT ID |
P80162 |
| EXPRESSION HOST |
HEK293 |
| TAG | |
| MOLECULAR CHARACTERIZATION |
Not available |
| MOLECULAR WEIGHT |
9.35 KDa |
| PURITY |
The purity of the protein is greater than 95% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining. |
| FORMULATION & RECONSTITUTION |
Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM PB, 150mM NaCl, 5% Trehalose, 1mM EDTA, pH 7.4. |
| STORAGE & SHIPPING |
Store at -20°C to -80°C for 12 months in lyophilized form. After reconstitution, if not intended for use within a month, aliquot and store at -80°C (Avoid repeated freezing and thawing). Lyophilized proteins are shipped at ambient temperature. |
| BACKGROUND |
Chemokine (C-X-C-Motif) Ligand 6 (CXCL6) is a small cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family. It is a potent neutrophil chemotactic and activating factor and it exhibits extensive similarity to other CXC chemokines such as IL-8 and ENA-78. CXCL6 can promote the release of MMP-9 from granulocytes indicating its potential role as an inflammatory mediator. It functionally uses both of the IL-8/CXCL8 receptors to chemoattract neutrophils but that is structurally most related to epithelial cell-derived neutrophil attractant-78 (ENA-78)/CXCL5. The human CXCL6 gene has been cloned and is physically mapped to the CXC chemokine locus on chromosome 4. Mature human CXCL6 is a 75 amino acid (aa) protein with a predicted molecular weight of approximately 8 kDa. Human CXCL6 shares 60% and 67% aa identity with mouse and bovine CXCL6, respectively. |
| USAGE |
Research use only |
1
/
의
1
Dima Biotech
SKU(재고 관리 코드):PME30076
Human CXCL6 (C-6His) Protein
Human CXCL6 (C-6His) Protein
PRODUCT DATA
IMAGES
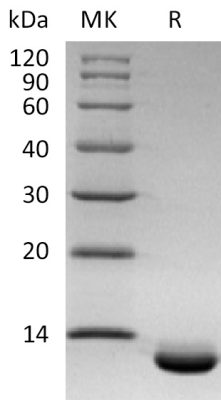
Figure 1. Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE.
Share


